Design of Control Unit
The Control Unit is classified into two major categories:
- Hardwired Control
- Microprogrammed Control
Hardwired Control
The Hardwired Control organization involves the control logic to be implemented with gates, flip-flops, decoders, and other digital circuits.
The following image shows the block diagram of a Hardwired Control organization.
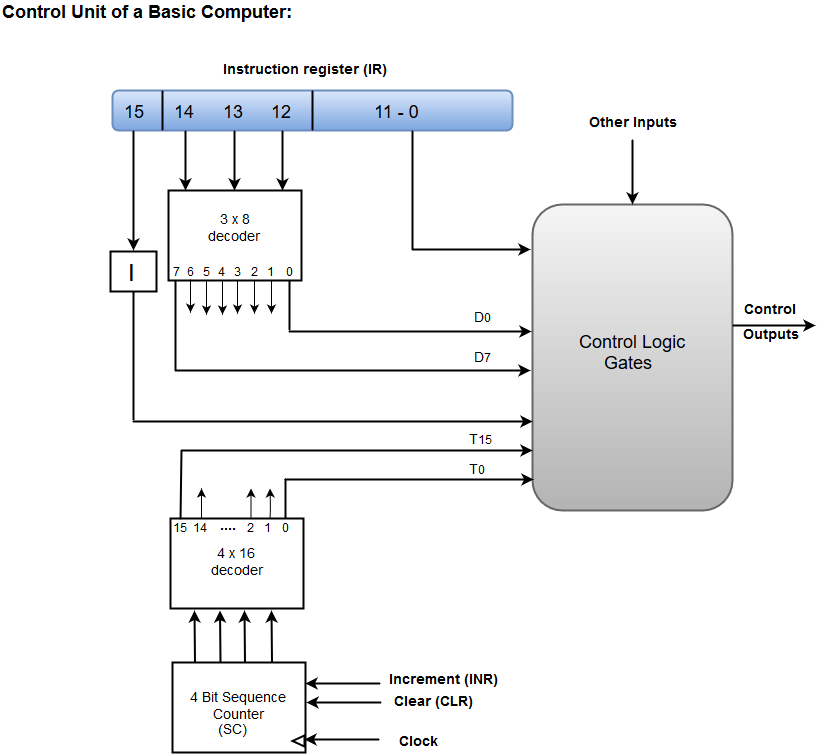
- A Hard-wired Control consists of two decoders, a sequence counter, and a number of logic gates.
- An instruction fetched from the memory unit is placed in the instruction register (IR).
- The component of an instruction register includes; I bit, the operation code, and bits 0 through 11.
- The operation code in bits 12 through 14 are coded with a 3 x 8 decoder.
- The outputs of the decoder are designated by the symbols D0 through D7.
- The operation code at bit 15 is transferred to a flip-flop designated by the symbol I.
- The operation codes from Bits 0 through 11 are applied to the control logic gates.
- The Sequence counter (SC) can count in binary from 0 through 15.
Micro-programmed Control
The Microprogrammed Control organization is implemented by using the programming approach.
In Microprogrammed Control, the micro-operations are performed by executing a program consisting of micro-instructions.
The following image shows the block diagram of a Microprogrammed Control organization.
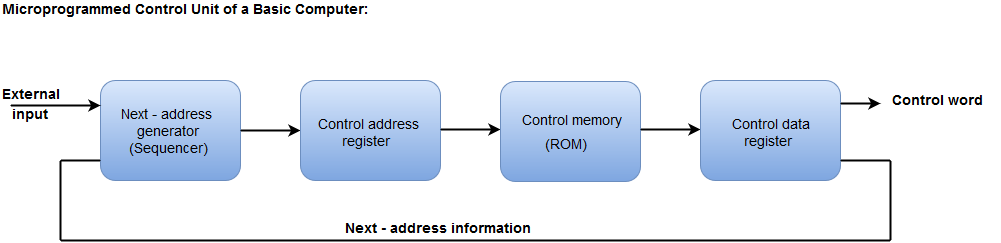
- The Control memory address register specifies the address of the micro-instruction.
- The Control memory is assumed to be a ROM, within which all control information is permanently stored.
- The control register holds the microinstruction fetched from the memory.
- The micro-instruction contains a control word that specifies one or more micro-operations for the data processor.
- While the micro-operations are being executed, the next address is computed in the next address generator circuit and then transferred into the control address register to read the next microinstruction.
- The next address generator is often referred to as a micro-program sequencer, as it determines the address sequence that is read from control memory.
Some Other Question :
- Explain the Common Bus System with its diagram.
- Explain the register transfer language with example.
- What is high impedance state in three-state buffer? Explain three state gate in designing bus system.
- Explain 4-bit Arithmetic Circuit with its Function Table
- Discuss the phases of Instruction Cycle with flowchart.
- Explain the basic working principle of the Control Unit of basic computer using diagram.
